The end is near for analogue radio... radio gets very high
 Brian Butterworth published on UK Free TV
Brian Butterworth published on UK Free TV One interesting characteristic of radio signal that are transmitted in the Medium Waveband is that the signal is carried in two ways, both of which are useful.
One is called a "ground wave", which means the signal follows the curve of the Earth. This means that the receiver and transmitter do not need to have a line-of-sight. So it is possible for a medium wave transmitter can serve a radio set 500 miles or more away. For example the old BBC World Service transmitter at Orfordness on 1296 kHz at 1.9MW could serve Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, north-east France and north-west Germany.
Another feature of Medium Waves that, at night, they also make "sky waves". After dark, the signals reflect off ionosphere (if the mid-layer ionization is strong) like a mirror. So, for example, Orfordness could be received in much of Europe at night. For this reason, AM radio station have to lower their power output after dark. Long Wave radio signals do not reflect.
The benefit to broadcasters of operating a low number of medium wave transmitter sites is offset against the need to guard for interference from other broadcasters long distances away. Even low-power stations daytime stations can become the source of interference many times their usual coverage area.
To this end, there has to be international co-ordination of frequencies and power output levels for Medium Wave and Long Wave. The agreements put stations at 9 kHz apart from each other. Between 531 kHz and 1611 kHz there are 118 "slots", 75 of which are used in some way in the UK. Some of these are for national "single frequency networks", such as Absolute Radio 1215 kHz and sometimes for a single fill-in station such as BBC Radio Scotland (AM) 585 kHz at 1.2kW at Dumfries.

The BBC gets high
The limitations of Medium Wave transmission didn't just limit the number of stations that could be broadcast. Spacing stations 9kHz also means that the there was a limit to the quality of sound, as human hearing ranges up to 2kHz, and the signals using AM were mono. Whilst the 9kHz range is fine for listening to a single human voice (Voice Fundamentals - Human Speech Frequency), it isn't very good for theFrequency Modulation was patented in 1933, but the BBC only started using the system for broadcasting radio in 1955. However this time the Very High Frequency range was used for transmission (from 88.0 to 94.6 MHz).
The FM provides a much better bandwidth - the mono signal goes up to 15 kHz. The system has also been enhanced by the addition of by two stereo "difference" signals, both 15 kHz wide, but this addition is susceptible to noise and multipath distortion and FM radios will flip back to mono when the signal is weak.
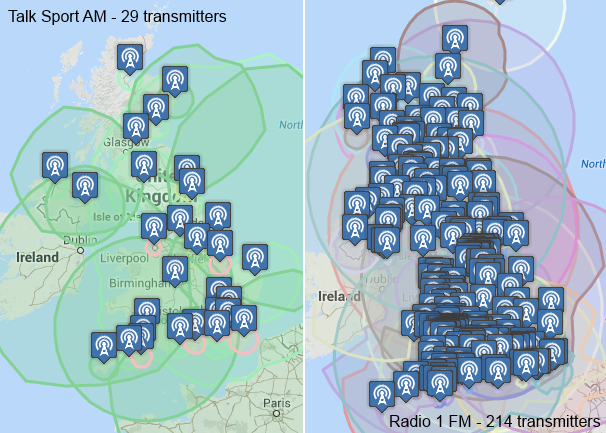
The benefit to the quality and reliability of an FM radio signal are clear, but the broadcaster has to provide a large network of lower power transmitters. For example, Radio 1 FM has 214 FM transmitters, whereas TalkSport, using the old Radio 1 MW network, has 29 AM transmitters.
However, the smaller wavelength of higher frequency transmitters means that FM transmitters can be mounted onto existing transmitter masts (such as those used for UHF television or mobile phone masts) and multiple services can be provided from the same location.
However, FM does have drawbacks. The initial design of the networks assumed that a rooftop aerial and home listening would occur. Most masts were changed to "mixed polarization" to allow for mobile and in-car listening.
FM took off when commercial radio started in the UK, and now most analogue listening is to VHF.
The benefits and drawbacks of FM
FM radio is seen by some as a "gold standard" of broadcasting.It is certainly true that compared to AM, with it "spooky sounds".
The CD is a good measure reference: with two-channel 16-bit PCM encoding at a 44.1 kHz sampling rate per channel, and thus a
FM/VHF is limited to 15 kHz, and the stereo signal is provided in two subcarriers, rather than as two independent signals (known as "joint stereo"). If the FM signal is weak the receiver will switch to the mono signal.
The addition of the RDS system FM transmission and to car radios means that modern in-car tuners can, using a second tuner, test all the possible reception frequencies for the channel being listen to and automatically switch to the best. This prevents frequent re-tuning whilst driving.
However, on main drawback remains: there are a limited number of national stations you can put out on FM. Radio 2 uses 88.1 to 90.2, which is 22 "slots", Radio 3 from 90.2 to 92.6, Radio 4 FM from 92.5 to 96.1 (as well as some of 103.5 to 104.9), Radio 1 from 97.1-99.8, Classic FM from 99.9 to 101.9, with a host of local stations using 96.2-97.0 and 102-107.9MHz.
You can explore the frequencies for yourself here:
List of all analogue radio frequencies - ukfree.tv
In the modern world, this limited choice has found solutions in digital radio.
More tomorrow in Part 3, where we look at the development of satellite, Freeview, online and DAB radios.
Thank you for putting up the spooky sounds video; that's exactly what I meant by MW sounds "hossily" after dark. From my experience, that tends to happen only after dark.
| link to this comment |
6:03 PM
Bristol
In the US they have something which I think is called sideband transmission stations. They offer sound radio that is encrypted as a subscription service, attached to a standard FM station.
Please could you explain how it works, what the sound quality is like and whether or not it has ever been used in the UK or Europe?
| link to this comment |
Charles's: mapC's Freeview map terrainC's terrain plot wavesC's frequency data C's Freeview Detailed Coverage
7:38 PM
Actually I do not believe the long medium and short wave frequencies have no future in broadcasting. Using DRM at these frequencies would be very attractive in that large areas can be covered with very few transmitters makeing it very cheap.
Your title that the end is nigh for analogue is just not true. The Government has never had any plans to close down FM. It has only proposed to close the BBC's main national stations.
DAB is dead long live FM.
| link to this comment |
8:15 PM
Seaford
The text said " Spacing stations 9kHz also means that the there was a limit to the quality of sound, as human hearing ranges up to 2kHz".
Surely 20kHz ?
| link to this comment |
David's: mapD's Freeview map terrainD's terrain plot wavesD's frequency data D's Freeview Detailed Coverage
8:36 PM
I thought that 1296kHz transmissions from Orfordness ceased in May 2012.
| link to this comment |
9:01 PM
The spooky sounds video sounded very "Delia Derbyshire" and BBC Radiophonic Workshop. I think that some of these spooky sounds were what gave Delia inspiration back in those heady days of the workshop!
Thanks for all the info. Radio still rocks!
| link to this comment |
10:04 PM
1296Khz and 648Khz-Main MW TX for western europe from orfordness closed 2 years ago
| link to this comment |
Steve Coombs: Sorry, yes.... I used the wrong tense. I have corrected.
| link to this comment |
... although the 1296kHz is still showing up in the Ofcom data ... Analogue radio on 1296kHz | ukfree.tv - 11 years of independent, free digital TV advice ?
| link to this comment |
Wikipedia says "Notionally, therefore, Baldock [meaning I think Babcock International Group] still retains the right to transmit from Orfordness on the other frequency (1296 kHz)." Orfordness transmitting station - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| link to this comment |